In earlier articles, we showed that the returns of most U.S. and international smart beta ETFs are primarily due to their dumb beta (dumb factor) exposures. Thus, smart beta ETFs turn out to actively time dumb beta factors. In fact, most smart beta strategies are primarily different approaches to sector rotation. After readers’ requests to extend the above analysis to relative returns and tracking error, we showed that the findings hold for U.S. smart beta tracking error. This article extends the analysis to international smart beta tracking error.
The results hold for international smart beta tracking error: Though some international smart beta ETFs do provide valuable exposures to idiosyncratic factors, most primarily re-shuffle basic dumb Region and Sector Factors. In fact, dumb beta exposures are even more influential for international smart beta equity ETFs than for their U.S. peers. Most international smart beta equity ETFs are mainly region and sector rotation strategies in disguise. Consequently, investors and allocators must guard against fancy re-packaging of dumb international risk factors as smart beta and should perform rigorous region and sector factor analysis of their smart beta allocations. Further, many international smart beta strategies can be substantially replicated and blended using simple passive Region and Sector Factors.
Measuring the Influence of Dumb Beta Factors on International Smart Beta ETFs
We used the same dataset of International Smart Beta Equity ETFs as our earlier article on international smart beta ETFs’ dumb factor exposures. We estimated monthly positions of each ETF and then used these positions to calculate portfolio factor exposures to traditional factors such as Regions and Sectors. These ex-ante factor exposures at the end of month m1 were used to predict returns during the subsequent month m2. We then calculated predicted and actual returns relative to the Global Equity Market (defined as the iShares MSCI ACWI Index Fund – ACWI). The correlation between actual and predicted relative returns quantified the influence of dumb beta factors on smart beta tracking error. The higher the correlation, the more similar a smart beta ETF is to a portfolio of traditional, simple, and dumb systematic risk factors.
The Influence of Region Beta on International Smart Beta ETFs
The simplest systematic risk factor to describe each security is its Region (Region Market Beta). Region Beta measures exposure to one of 10 broad regional equity markets (e.g., North America, Developing Asia). These are the most basic and cheap passive international factors. Even this single-factor model estimated with robust statistical techniques delivered 0.67 mean and 0.68 median correlations between predicted and actual relative returns:
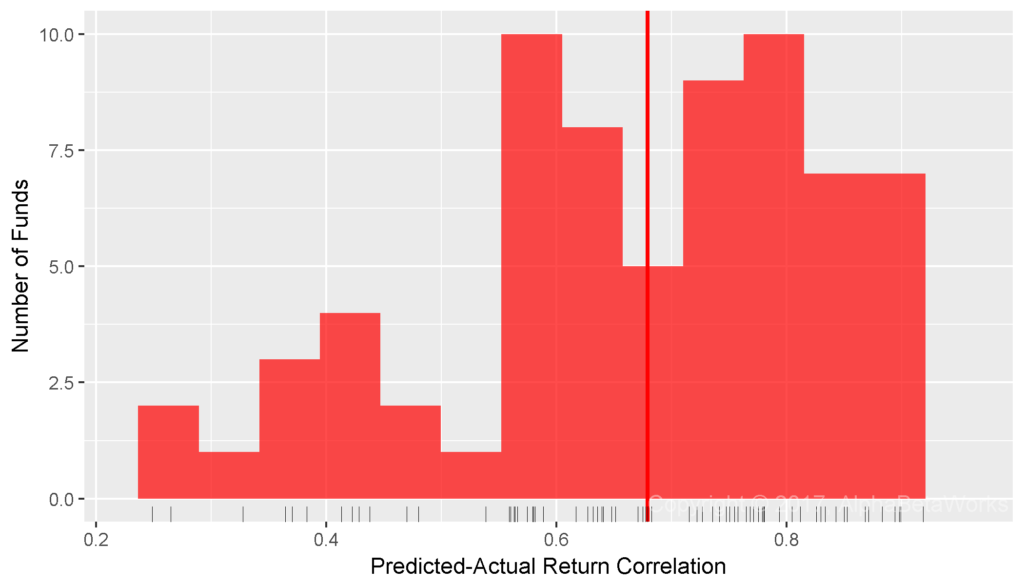
International Smart Beta Equity ETFs: Correlation between relative returns predicted using Region Factors and actual relative returns
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 0.2490 0.5662 0.6791 0.6655 0.7805 0.9185
For a quarter of smart beta ETFs, Region Factor alone replicates 61% (0.7805²) of tracking error. For this group of strategies, international smart beta tracking error is largely due to region rotation.
The Influence of Region and Sector Betas on International Smart Beta ETFs
We next extended the model with Sector Factors. Sector Beta measures exposure to one of 10 broad sectors (e.g., Energy, Technology). Region and Sector Betas, estimated with robust methods, delivered 0.75 mean and 0.77 median correlations between predicted and actual relative returns:
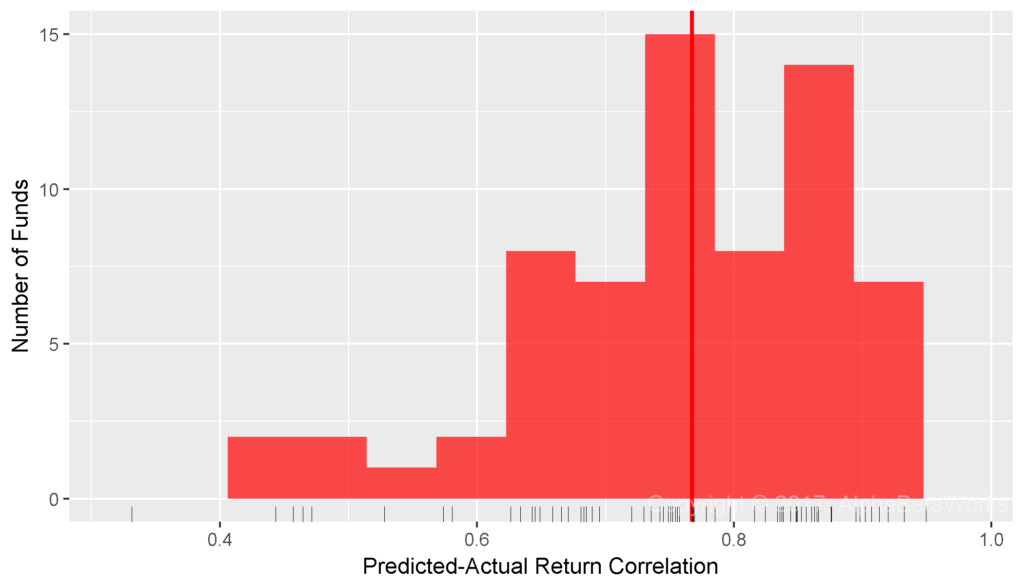
International Smart Beta Equity ETFs: Correlation between relative returns predicted using Region and Sector Factors and actual relative returns
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 0.2604 0.6807 0.7673 0.7461 0.8523 0.9494
For most international smart beta ETFs, Region and Sector Factors replicate 59% (0.7673²) of tracking error. Thus, for most international smart beta equity ETFs, over half of tracking error is due to region and sector rotation.
International Smart Beta Variance and International Dumb Beta Variance
Rather than measure correlations between relative returns of replicating dumb beta portfolios and ETFs, we can instead measure the fractions of their (relative) variances unexplained by dumb beta exposures. The Dumb Beta Variance (in red below) is the distribution of ETFs’ relative variances due to their dumb Region and Sector Factor exposures. The Smart Beta Variance (in blue below) is the distribution of ETFs’ relative variances unrelated to their dumb beta exposures:
International Equity Smart Beta ETFs: Percentage of tracking error explained and unexplained by the Region and Sector dumb beta exposures
Percentage of international equity smart beta ETFs’ relative variances due to dumb beta exposures:
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 6.78 46.34 58.88 57.70 72.65 90.13
Percentage of international equity smart beta ETFs’ relative variances unrelated to dumb beta exposures:
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 9.87 27.35 41.12 42.30 53.66 93.22
For a quarter of strategies, over 2/3 of international smart beta tracking error is due to region and sector rotation, and for some, it reaches 90%.
Our analysis focused on the most basic Region and Sector Factors and excluded Value/Growth and Size Factors, which are decades old and also considered dumb beta by some. If one expands the list of dumb beta factors, smart beta variance shrinks further.
Conclusions
- Traditional, or dumb, Region and Sector Betas account for the majority of international smart beta tracking error.
- Smart beta effects, unexplained by the traditional Region and Sector Betas, account for 41% of variance or less for most international smart beta ETFs.
- With proper analytics, investors and allocators can identify products that do provide unique international smart beta exposures and can guard against fancy re-packaging of dumb international beta.
- Investors and allocators can monitor the majority of international smart beta ETF relative risk by focusing on their Region and Sector Factor exposures.
- Most international smart beta strategies can be combined using Region and Sector Factor portfolios.